概要
本文跟大家一起探讨一下 Java 枚举的本质,这篇文章的内容是我在 2012年09月05日 发布到 CSDN 上面的一篇博文 Java 枚举:理解枚举本质,虽然已经不在 CSDN 上面耕耘了,但偶尔也会去看看朋友们的留言,毕竟感情在那里!今天偶然看到有小伙伴评论这篇文章,一时兴起就想再次分享给大家。
学习编程语言,会用只是最基本的要求,了解和熟悉其实现、运行机制才使得你有别于常人!
C 枚举
在 C 语言中,可以这样来定义枚举,如下示例:
1 | enum color { |
关键字 enum 定义枚举,在定义枚举的同时,声明该枚举变量 col.
注意:C 语言中枚举成员的值是根据上下文自动加 1 的(GREEN = 1,BLUE = 2 等)。
C 语言中 switch 语句支持枚举类型,如下示例:
1 |
|
Java 枚举
那么,Java 里面的枚举与其类似,但是又不是完全一样。Java 语言中定义枚举也是使用 enum 关键字,如下示例是 Java 语言的枚举:
1 | public enum Color { |
上述定义了一个枚举类型 Color(可以说是类,编译之后是 Color.class).
上面的定义,还可以改成下面的这种形式:
1 | public enum Color { |
到这里你可能会觉得迷茫(如果你是初学者的话),为什么这样子也可以,why?
其实,枚举的成员就是枚举对象,只不过它们是静态常量而已。
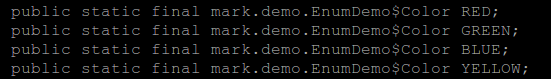
使用 javap 命令(javap 文件名<没有后缀.class>)可以反编译 class 文件,如下:
我们可以使用普通类来模拟枚举,下面定义一个 Color 类,如下:
1 | public class Color { |
结合上图反编译的结果,做一下对比,你是否看出了一点端倪(坏笑),如果没有看出来,那就接着往下看吧。
如果按照这个逻辑,是否还可以为其添加另外的构造方法?答案是肯定的!
1 | public enum Color { |
为 Color 声明了两个成员变量,并为其构造带参数的构造器。
如果你这样创建一个枚举:
1 | public enum Color { |
编译器就会报错:
1 | The constructor EnumDemo.Color(String, int) is undefined |
到此,你应该看明白了,枚举和普通的 Java 类很像。
对于类来讲,最好将其成员变量私有化,并且为成员变量提供 get、set 方法。
按照这个原则,可以进一步写好 enum Color,如下示例:
1 | public enum Color { |
但是 Java 设计枚举的目的是提供一组常量,方便开发者使用。如果我们冒然的提供 set 方法(外界可以改变其成员属性),好像有点违背了设计的初衷。
那么,我们应该舍弃 set 方法,保留 get 方法。
1 | public enum Color { |
对于普通的基本类可以将其实例化,那么,能否实例化枚举呢?
在回答这个问题之前,先来看看 Color.class 文件:
1 | public static enum Color { |
可以看出,编译器淘气的为其构造方法加上了 private,那么也就是说,我们无法实例化枚举。
所有枚举类都继承了 Enum 类的方法,包括 toString、equals、hashcode 等方法。因为 equals、hashcode 方法是 final 的,所以不可以被枚举重写(只可以继承),但可以重写 toString 方法。
文末的附录中提供了 Enum 的源码,有兴趣可以查看阅读!
那么,使用 Java 的类来模拟一下枚举,大概是这个样子:
1 | package mark.demo; |
附录
Enum.java
1 | package java.lang; |
扫码关注,你我就各多一个朋友~
